PREVENTIVE MEDICINE CONFERENCE 2021
ABOUT CONFERENCE
After successful accomplishment of our 11thEdition of International Conference on Preventive Medicine and Public Health on June 25, 2020. We take colossal delight to welcome you at our new destination in Amsterdam, Netherlands from April 19-20, 2021 for our upcoming Event on 12thEdition of International Conference on Preventive Medicine and Public Health organized by Euroscicon Pte Ltd. (Preventive Medicine Conference 2020).
Euroscicon is honoured to host the 12th Edition of International Conference on Preventive Medicine and Public health taking place on April 19-20, 2021 in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The ICPMPH 2020 has turned in to a premier forum to network, learn and connect with experts, academicians, researchers, specialists and activists in generating a platform to discuss and spread meaningful messages, values and practices in the subject of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.
The conference is hosted around the theme "Emphasize on recent advancements in preventive medicine and public health to strife against COVID-19.” with the goal to unite a wide audience of academics, industry, policymakers, and specialists around clearly circumscribed topics, engage participants in the productive level-headed discussion, and facilitate mutual understanding. An additional objective of the Congress is to provide a place for academicians and experts with inter-disciplinary/multi-disciplinary interests associated to Preventive Medicine and Public Health to meet and interact with individuals inside and outside their own specific disciplines.
We are looking forward to welcoming you and spending valuable time in Amsterdam, Netherlands.
What you'll get:
• Get deep and deeper than ever into Preventive Medicine and Public Health obstruction with 2 full days of expert keynotes, plenaries, workshops, symposiums, and group discussions.
• Develop a plan of action and long-term strategies you can implement in your organization/institutions
• Learn new emerging technologies, the latest trends, and success strategies around individual genomics, preventive medicine policies, risk management, diagnostics, immunotherapy, analytics, infrastructure and more.
• Network with expert peers, medical leaders, and Preventive Medicine specialists, and get the insights you need to move forward for better advancement and development.
• Get access to focused and provocative discussions.
• Engage in an interactive environment on key issues.
Target Audience:
The conference is open for all the professionals and experts working in Preventive Medicine and Public Health which includes but not limited to:
Preventive Medicine and Public Healthcare professionals, Public Healthcare Consulting firms, Preventive medicine and Public Healthcare providers, Preventive Medicine and Public Healthcare recruiting agencies, Public Healthcare Administrators, Physicians, Business Analysts, Data Analyst, , Healthcare head seekers, Healthcare Investors, Preventive Medicine and Public Health specialists, Public Health Workers, Preventive Medicine and Public Health Societies /NGO’s, Preventive Medicine and Public Organizations, Public Health Professionals, Preventive Medicine and Public Health Economists, Medical Lab Technicians, Community Health Workers, Primary Care Providers, Foundation Leaders, Direct Service Providers, Policy makers, Researchers, Academicians, Advocates Policymakers and others.
Call for Abstracts are open for Key Note Forum, Oral performances, panel presentations and scientific posters across the list of tracks highlighted in our website and papers on other topics not listed are also welcome if they meet the objectives of the conference. We hope and anticipate ICPMPH 2021 theme to inspire a number of research avenues and look forward to discussing ideas, new researchers, findings, and synergies, in this International Academic Forum.
We hope to meet you in Amsterdam, Netherlands this April 2021!
SESSIONS/TRACKS
Track 01: Preventive Medicine and Public Health
Preventive Medicine and Public health are about helping individuals to remain healthy and save them from threats to their health. Public health is concerned with protecting the health of entire populations. It offers the prevention of disorders and to promote the health of people. Public Health is a part of sciences, skills, and convictions that is focused on the preservation. The aim of public health is to raise the quality of life through prevention and treatment of disease, including psychological health. This is done through the examination of cases and health indicators, and through the promotion of healthy behaviors. Public health is concerned with the health of the whole population and the prevention of disease from which it suffers. It is also one of the efforts organized by society to protect, promote, and restore the peoples’ health. Public health activities include helping individuals; at different circumstances, they include managing more extensive components that affect the strength of numerous individuals (for example an age-group, an ethnic group, a locality, or a country). The outcome of Public health observation is the identification and prioritization of public health issues the world is facing today, including HIV/AIDS, antibiotic resistance, diabetes, zoonotic diseases, and waterborne diseases. Preventive Medicine and Public healthincorporate the interdisciplinary methodologies of epidemiology, biostatistics and health services.
Track 02: Preventive Medicine and Occupational Health
Preventive Medicine and Occupational healthis a master branch of medicine that focuses on the physical and mental health of employees in the working environment. Occupational health professionals intend to discover what impact work has on staff health and make sure that staff is fit to undertake the role they are employed to do both physically and emotionally. The aim of occupational health is to prevent business related disease and injury by empowering safe working practices; monitoring the health of the workforce; supporting the administration of sickness absence. Occupational healthexperts can support associations by advising on business-related diseases and accidents, carrying out assessments for new starters and existing workers, observing the health of representatives and prevention. The maintenance and promotion of the mental, social and physical well-being of all the workers belonging to all the categories is the goal of Preventive Medicine and Occupational Health. This leads to prevention of departures from health issues, control of risks and the adaptation of people to their jobs and works to people. This incorporates all the fields of healthcare concerned about helping an individual to fulfill the demands of their work environment, with their health under concern. Occupational physicians must have a wide information of medication and be competent in various vital zones. They often advise global bodies, governmental and state agencies, associations and trade unions. There are contextual links to physical medicine and recovery and to insurance medicine.
Track 03: Preventive Medicine and Diabetes
Diabetes often alluded to by doctors as diabetes mellitus. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Glucose originates from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that allows the glucose to get into your cells to give them vitality. With Type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With Type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or utilize insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose remains in your blood. You can also have pre-diabetes. This implies that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Having pre-diabetes puts you at a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
Over time, having excessively glucose in your blood can cause serious issues. It can affect and harm your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can cause coronary illness, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant ladies can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes. Blood tests can show if you have diabetes. One kind of test, the A1C, can also check on how you are dealing with your diabetes. Exercise, weight control and adhering to your diet plan can help control your diabetes. You should also monitor your blood glucose level and take medicine if recommended.
Track 04: Preventive Medicines and Vaccines
Vaccinations or Immunization are an indivisible part of preventive medicine against microbial infections, like measles, diphtheria, tetanus, hepatitis, smallpox, polio etc. A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides dynamically acquired immunity to a particular disease. Immunization, adjournment of weakened, killed, or divided microorganisms or of antibodies or lymphocytes that is controlled primarily to anticipate disease.
A vaccine can confer dynamic immunity against a particular harmful agent by stimulating the immune system to attack the agent. Once invigorated by an Immunization, the antibody-producing cells, termed as B lymphocytes, stay sensitized and ready to react to the agent should it ever gain entry to the body. A vaccine may confer passive immunity by providing antibodies or lymphocytes already made by an animal or human donor. Immunizations are usually administered by injection (parenteral administration), but some are given orally. Vaccines applied to mucosal surfaces, such as those lining the gut or nasal passages, appear to invigorate a greater antibody response and may be the most effective route of administration.
Track 5: Preventive Medicine and Chronic Diseases
Chronic disease crisis is an enormous threat around the globe currently, which has been brought about by risk factors that are preventable.
Chronic disease is a disease that persists over a long period of time. Chronic disease can hinder independence and the health of individuals with disabilities, as it might create additional activity limitations. People with chronic disease often think that they are free from the disease when they have no symptoms. Having no symptoms, however, does not necessarily mean that chronic disease has disappeared. Chronic diseasestend to become more common with age. Chronic diseases in developed countries include arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, heart attacks, stroke, cancer (colon and breast cancer), obesity, diabetes etc.
The good news is that chronic disease can be prevented or controlled through 1) regular participation in physical activity, 2) eating healthy, 3) not smoking, and 4) avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
Track 06: Preventive Medicine and Geriatrics
Geriatrics is a specialty that focuses on health care of elderly individuals. The art and science of preventing diseases in the geriatric population and promoting their health are termed as Geriatrics. The geriatric titans are the infirmity that is shown up in the aging public, particularly as they start to fail. These incorporate immobility, instability, incontinence and impaired intellect. Its objective is to promote health by preventing and treating diseases and disabilities in older adults. There is no static age at which patients might be under the care of a geriatrician or geriatricdoctor who requires in the care of elderly individuals. Impaired vision and hearing loss are the most common chronic problems among the Geriatric population.
Track 07: Preventive Medicine and Community Health
Community health and preventive medicine focus on determining how to prevent diseases. A community is a group of people who might have different characteristics but share geographical location, settings, goals, or social interest. Examples of communities include people living in the same town, members of a church, or members of a sports team. Community health is a field of public health that focuses on studying, protecting, or improving health within a community. Promoting human health and reducing health risks through disease prevention, education and other public health services are the major goals of Preventive Medicine and Community Health. It does not focus on a group of people with the same shared characteristics, like age or analysis, but on all people within a geographical location or involved in the specific activity.
Community health covers a wide range of health care interventions, including health promotion, disease prevention, and treatment. It also involves management and administration of care. Community health workers (CHWs) are often frontline health professionals with knowledge of specific characteristics and developments of the community. They are often members of the community themselves and play an important role in the functioning of community care.
Track 08: Preventive Medicine and Internal Medicine
Internal medicine, the medical field deals with the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of adult diseases. The significant objective of Internal Medicine is to prevent and treat the diseases, in turn increasing the lifespan. Doctors specializing in internal medicine are called internists. Internists are skilled in the management of patients who have undistinguishable or multi-system disease procedures. Internists care for hospitalized and ambulatory patients and may play an important role in teaching and research. Subspecialties of internalmedicineincorporate oncology, infectious diseases, endocrinology, allergy, immunology, cardiology, nephrology, and rheumatology etc.
Track 09: Preventive Medicine and Primary Care
Primary care is that care provided by specialists, experts absolutely trained for and skilled in broad first contact and continuing care for individuals with any undiagnosed sign, symptom, or health concern not limited by problem origin (biological, behavioral, or social), organ system, or diagnosis.
Primary care comprises disease prevention, patient education, health promotion, health maintenance and treatment of acute and chronic illnesses in a variety of healthcare situations. Primary care is executed and governs by a personal specialist often collaborating with other health professionals, and utilizing discussion or referral as appropriate. Primary care provides patient advocacy in the health care system to achieve cost-effective care by coordination of healthcare amenities. Primary careencourages effectual communication with patients and inspires the role of the patient as a companion in health care.
Track 10: Preventive Medicine and Oncology
The word Oncology is derived from Greek ónkos means tumor and logos mean study. Oncology is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. It involves therapeutic oncology (use of chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and other drugs to treat cancer), radiation oncology (use of radiation therapy to treat cancer), and surgical oncology (use of surgery and other procedures to treat cancer). The person who treats cancer diseases is known as an oncologist. In simple words, we can define that the study of cancer is oncology. There are different types of cancer like Breast cancer, Prostate cancer, Basal cell cancer, Lung cancer, Leukemia, Lymphoma and Colon cancer. Cancer is a form of disease where the cancer-causing cell will invade (cell start to grow out of control) and spread to other body parts.
Track 11: Preventive Medicine and Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi. The Infectious diseases can be transmitted, directly or indirectly, from one individual to another. They are harmless and even helpful, but under certain circumstances, they may cause disease. Zoonotic diseases are infectious diseases of animals that can cause disease when transmitted to humans. Some infectious diseases can be transmitted from individual to individual. Some are transferred by bites from insects or animals. And others are acquired by consumption of contaminated food or water which is being exposed to organisms in the environment.
Signs and symptoms differ depending on the organism causing the disease; however frequently incorporate fever and fatigue. Gentle diseases may respond to and home treatment, while some serious threatening diseases may require hospitalization. Numerous infectious diseases, such as measles and chickenpox, can be prevented by vaccines. Frequent and thorough hand-washing also helps protect us from most infectious diseases.
Track 12: Ebola Virus Disease
Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal illness in humans. Ebola virus disease is caused by four different strains of Ebola virus; these viruses infect humans and nonhuman primates. The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission. The virus family Filoviridae includes three genera: Cueva virus, Marburg virus, and Ebola virus. Within the genus Ebola virus, five species have been identified: Zaire, Bundibugyo, Sudan, Reston and Taï Forest. The first three, Bundibugyo ebola virus, Zaire ebola virus, and Sudan ebola virus have been associated with large outbreaks in Africa. The virus causing the 2014–2016 West African outbreak belongs to the Zaire ebola virus species.
Ebola is introduced into the human population through close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected animals such as chimpanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys, forest antelope and porcupines found ill or dead or in the rainforest. Ebola then spreads through human-to-human transmission via direct contact (through broken skin or mucous membranes) with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected people, and with surfaces and materials (e.g. bedding, clothing) contaminated with these fluids.
Symptoms of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) are treated as they appear. When used early, basic interventions can significantly improve the chances of survival. These include:
- Providing fluids and electrolytes (body salts) through infusion into the vein (intravenously).
- Offering oxygen therapy to maintain oxygen status.
- Using medication to support blood pressure, reduce vomiting and diarrhea and to manage fever and pain.
- Treating other infections, if they occur.
Recovery from EVD depends on good supportive care and the patient’s immune response. Those who do recover develop antibodies that can last 10 years, possibly longer. It is not known if people who recover are immune for life or if they can later become infected with a different species of Ebola virus. Some survivors may have long-term complications, such as joint and vision problems.
Track 13: Personalised and Precision Medicine
Personalized medicine, also known as precision medicine, is a therapeutic method that segregates patients into various classifications—with medical results, practices, interventions or products being couturier to the individual patient based on their anticipated response or risk of disease.
Customized prescription, named as exactness solution, is a therapeutic strategy that isolates patients into various classifications—with medicinal outcomes, practices, interventions or items being custom-made to the individual patient in light of their foreseen reaction or danger of sickness. The terms customized drug, accuracy prescription and P4 medication are utilized conversely to portray this origination however a few creators and associations utilize these articulations independently to show specific refinements.
Track 14: Preventive Medicine and Dentistry
Dentistry, a branch of medicine which deals with the prevention, study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and circumstances of the oral cavity, generally in the dentition but also the oral mucosa, and of contiguous and related structures and tissues, particularly in the maxillofacial region. Though fundamentally associated with teeth among the over-all public, the arena of dentistry is not constrained to teeth, however, integrates individual parts of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint and other supportive, nervous, lymphatic, muscular etc.
Dental treatments are conceded out by a dental group, which frequently comprises of a dental specialist and dental auxiliaries. Maximum dental specialists either work in private practices, dental hospitals or organizations.
Track 15: Preventive Medicine and Cardiology
Cardiology a branch of medicine deals with disorders of the heart as well as parts of the circulatory system. This field includes medical analysis and treatment of congenital heart defects, heart failure, valvular heart disease, coronary artery disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists. A cardiologist is not the same as a cardiac surgeon. A cardiac surgeon performs open heart surgery.
A cardiologist concentrates on diagnosing and treating diseases of the cardiovascular system. The cardiologist carries out tests and may do procedures, such as angioplasty, heart catheterizations, or inserting a pacemaker. Heart disease relates exactly to the heart, while cardiovascular disease affects the heart, the blood vessels, or both.
Track 16: Preventive Medicine and BehavioralHealth
Behavioral health refers to a person’s state of being and how their behaviors and choices affect their general wellbeing and health. Substance abuse and obsessions of all kinds fall into the realm of behavioral health. Behavioral health disorders are diseases that are invigorated or spread by your sensible decisions and which you are incapable to resist the urge to recurrence, in spite of negative significances. Changing these uncontrollable behaviors straightforwardly impacts your life, then, by lessening or eliminating some of the indicators of the behavioral health disorder.
Behavioral health indicates mental and emotional well-being. From those struggling with psychological sicknesses – such as depression or personality disorder – to those with substance abuse disorders or other addictive behaviors, treatment is vital to reclaiming control of their lives.
Track 17: Psychology and Psychiatric Disorders
Psychology is the methodical study of the mind and behavior. Psychology is a multifaceted discipline and incorporates many sub-fields of study in such regions as human development, sports, health, clinical, social conduct, and intellectual procedures. The discipline of psychology is broadly categorized into two subdivisions: a vast profession of consultants and a smaller but growing science of mind, brain, and social behavior. The two have distinctive objectives, training, and practices, yet a few analysts incorporate the two.
The term psychiatric disorders are sometimes used to refer to what is more frequently known as mental disorders or psychological disorder. Psychiatric disorders are patterns of behavioral or psychological side effects that affect different areas of life. These disorders create distress for the individual experiencing these symptoms.
A psychiatric disorder may also cause physical manifestations, for example, a headache, back pain, or stomach pain. In case if you’re being assessed for a psychiatric disorder, make sure to inform your doctor regarding any physical side effects you're having, including unexplained aches and pains.
Track 18: Preventive Medicine and Family Medicine
Family medicine (FM), formerly family practice (FP), is a medical specialty devoted to comprehensive health care for people of all ages; the specialist is named a family physician or family doctor. In Europe the discipline is often referred to as general practice and a practitioner as a general practice doctor or GP; this name emphasizes the holistic nature of this specialty, as well as its roots in the family. Family practice is a division of primary care that provides continuing and comprehensive health care for the individual and family across all ages, genders, diseases, and parts of the body; family physicians are often primary care physicians. It is based on knowledge of the patient in the context of the family and the community, emphasizing disease prevention and health promotion. According to the World Organization of Family Doctors (WONCA), the aim of family medicine is to provide personal, comprehensive, and continuing care for the individual in the context of the family and the community.
Track 19: Preventive Medicine and Nutrition
The importance of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition is recognized widely. Preventive Medicine and Nutrition cover all aspects of wellness, including diet, genetic variation, and stress management. A sense of responsibility is gained for lifestyle choices and their effects upon one’s health are considered with concern. Nutrition, nourishment, or ailment, is the supply of food materials required by organisms and cells to remain alive. In science and human medication, nutrition is the science or practice of consuming and utilizing foods.
In hospitals, nutrition might refer to the food requirements of patients including nutritious arrangements conveyed by methods of an IG (intragastric) or IV (intravenous) tube. Nutritional science considers how the body breaks food down (catabolism) and how it repairs and forms tissue and cells (anabolism). Catabolism and anabolism combined together and referred to as metabolism. Nutrition emphases on how diseases, circumstances, and problems can be prevented or reduced with a healthy diet. Similarly, nutrition involves recognizing how certain diseases and circumstances might be caused by dietary factors, such as food intolerances, poor diet, and food allergies.
Track 20: Preventive Medicine and Hospital Medicine
Hospital medicine is a sort of practice within internal medicine in which the clinical focus is caring for hospitalized patients. Internists practicing hospital medicine are frequently called “hospitalists.” Although not all hospitalists are required to be internists, the nature of internal medicine training uniquely makes internists for hospital medicine practice. As a result, the vast majority of hospitalists are trained in internal medicine, usually general internal medicine.
The discipline of hospital medicine grew out of the increasing complexity of patients requiring hospital care and the need for dedicated clinicians to oversee their management. The hospitalist model succeeded the traditional method of caring for hospitalized patients, which was often done by clinicians also seeing ambulatory patients or with other clinical obligations that limited their ability to provide the intensity of care often required by these patients. By focusing their practice on this specific group of patients, hospitalists gain specialized knowledge in managing very ill patients and are able to provide high-quality, evidence-based, and efficient patient and family-centered care in hospital settings.
Track 21: Preventive Medicine and Adolescent Medicine
Adolescence is a developmental period and a time of rapid and complex physical, intellectual, emotional, and social development. It is a critical stage in life as young people mature from childhood, when they are dependent on parents and other adults, to young adulthood when they are expected to make decisions and be responsible for themselves.
Adolescents have many concerns about their changing bodies, changing moods, and changing interactions with others. They have concerns about what is normal and what they should expect as they continue to mature. They engage in behaviors that may present risks to their health and safety. Parents also have concerns about what to expect of their adolescent children, what is normal and how they can be kept safe and healthy.
Track 22: Preventive Medicine and Sport Medicine
Sports medicine emphases on helping individuals improve their athletic performance, recover from injury and avoid future injuries. It is a fast- developing healthcare field because health workers who specialize in sports medicine help a wide range of individuals, not just athletes.
Sports medicine specialists have the unique training to restore function to injured patients so they can move again as soon as possible. They are also knowledgeable about preventing illness and injury in dynamic individuals. Although sports medicine specialists do work with professional athletes, they also treat children and adolescences involved in sports and adults who exercise for personal fitness, as well as individuals who have physically demanding jobs, like construction workers.
Track 23: Preventive Medicine and TeleMedicine
Telemedicine is generally a new concept, and in the realm of the internet, it develops with lightning speed. Telemedicine is a subset of telehealth, which incorporates both remote clinical administration conveyance and nonclinical components of the healthcare system. In contrast, telemedicine alludes particularly to the utilization of medical information exchanged for the purpose of improving a patient's health. Telemedicine is the remote conveyance of healthcare services, such as health assessments or consultations, over the telecommunications infrastructure. It allows healthcare providers to evaluate, diagnose and treat patients utilizing regular innovation, such as video conferencing and smartphones, without the requirement for an in-person visit. It is often a time-saving way for a consumer to see and speak to a clinician for minor and non-urgent medical needs instead of going to a primary care physician's office or emergency department.
MARKET ANALYSIS
Introduction:
The major goal of preventive medicine is the absence of disease, be it by preventing the occurrence of a disease or by halting a disease thereby reducing the resulting complications after its onset. The challenge that is faced by preventive medicine is to motivate the individual to make prevention a practice. The measure taken for disease prevention and health promotion is called preventive medicine, as way round opposite to treatment of symptoms and diseases. Just as health encompasses a variety of physical and mental states, so does disease, which is affected by lifestyle, external or genetic factors. Disease prevention is subject to on anticipatory actions that can be arranged as essential, optional, and tertiary prevention.
Market Scenario and Overview:
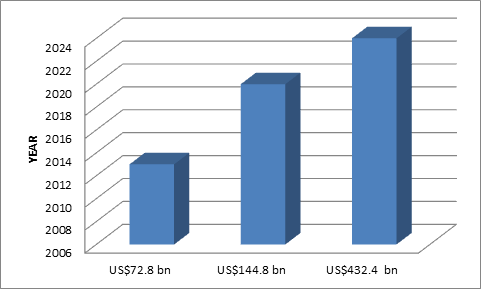
Preventive Medicine Market is isolated topographically into regions Western Europe, Eastern Europe, North America, Latin America, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East. North America is the biggest and fastest developing business sector for preventive healthcare technologies and services during the forecast period of 2014 to 2020. Asia-Pacific and the Middle East and others are experiencing low growth now but are expected to gain potential markets in the coming future. The expectation of the global preventive medicine market is to reach USD 432.4 billion by 2024. The market is expected to extend at a 9.70% CAGR from 2014 to 2020, with its value rising from US$72.8 billion in 2013 to US$144.8 billion by 2020.
Source: Preventive Medicine Euroscicon, 2020 Internal
Regional Analysis of Preventive medicine and Public Health Services
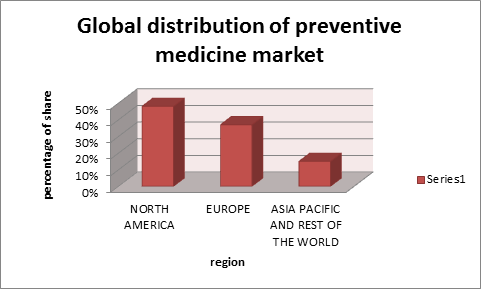
USA: North America being the biggest and the fastest developing region is fuelled by growing awareness, supportive reimbursement policies, and the presence of several leading players. Currently, North America holds almost half of the global market share with 48 % and is expected to continue to dominate in the forecast too.
Europe: Europe is the second largest for preventive healthcare market and services. High healthcare spending per capita and developed economies and in countries like Germany and France are the driving factors for market growth in the region. European preventive market is able to grow because of the achievements of the high-risk factor epidemiology in the region. Europe holds 37% of the global market share.
The Middle East and Asia Specific: Asia-Pacific and Rest of the World are expected to be potential markets in the future, with the current market estimated to be low, holding only 15% of the share.
Source: Preventive Medicine Euroscicon, 2020 Internal
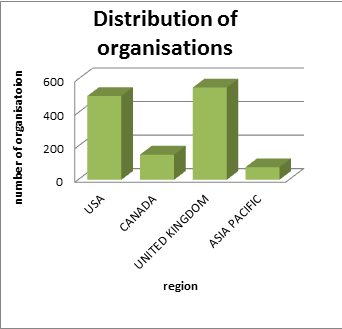
Key Players in Preventive Medicine and Public Health Market:
Top Preventive Medicines Organisations
Counsyl, Inc., USA, Huneo, USA, Omada Health, USA, Health Tap, USA, GlaxoSmithKline Plc. USA, Linde Group, Germany, Omron Healthcare, Japan, Philips Healthcare, Netherlands, McKesson Corporation, U.S., Kindred Healthcare, U.S., Abbott Laboratories, U.S., Kinnser Software, Inc., U.S., A&D Company, Japan, Fresenius SE & Co. KGaA Germany, Apria Healthcare Group, U.S., Kinnser Software, Inc., U.S., Journal Of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.
Source: Preventive Medicine Euroscicon, 2020 Internal
Top Preventive Medicines Institutions:
Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, University of Iowa, Iowa City, Iowa University of Illinois, Chicago, Illinois, University of Alabama, Birmingham, Alabama George Washington University, Washington, D.C., University of Texas , Houston Health Sciences Centre, Houston, Texas ,Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, Tulane University, New Orleans, Louisiana University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Penn Sylvia Boston University, Boston, Massachusetts University of California, Los Angeles California University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Berkley Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine, London Imperial College London, London , The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, London, Lister Institute of Preventive Medicine, UK, The Leibniz Institute for Prevention Research and Epidemiology, Bremen Danube University Krems, Austria University of East Anglia, Anglia.
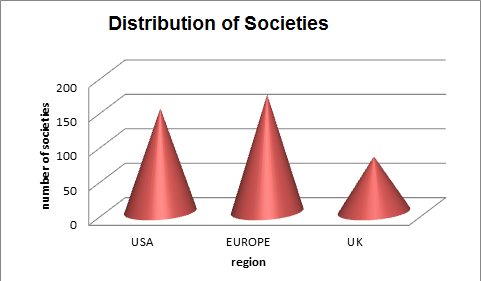
Top Healthcare Societies:
European society of preventive medicine, Europe, Preventive Medicine Society, Europe, Joint British Society, England, British Geriatrics Society, England, Society for Veterinary Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine (SVEPM), Europe, European medical association, Europe, European Union geriatric medicine society, Europe, European lifestyle medicine association, Europe, Aerospace medical association, USA, Association for prevention and research, Europe, The American Society for Preventive Cardiology, USA, Medical Society Consortium on Climate and Health, USA, The Centre for Medicine, Society and Prevention, USA, International Academy of preventive medicine, Europe Preventive Medicine Organisation, USA, Italian Society of Hygiene, Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Italy, Wilderness Medical Society practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of frostbite.
source: Preventive Medicine Euroscicon, 2020 Internal
Conclusion:
Preventive Medicine and Public Health market have a lot to a proposal to the Preventive Medicine Experts, pharmaceutical producers, Physicians, Public Health professionals, etc. It has already made an impact in developed countries like Europe, USA, Canada, and Australia.
Development of the market, the distribution of knowledge can only occur through international meetings and conferences. The 11th Edition of International Conference on Preventive Medicine and Public health happening on June 22-23, 2020 in Zurich, Switzerland will address the recent advancements happening in this field with a series of Key Notes, Plenary sessions, Workshops, Symposiums and discussions represented by eminent speakers from more than 40 nations.
Disclaimer:
The statistics developed in this report is intended only for the purpose of understanding the scope of hosting related international meetings at the respective locations. This information does not constitute managerial, legal or accounting advice, nor should it be considered as a corporate policy guide, laboratory manual or an endorsement of any product, as much of the information is speculative in nature. Conference Organizers take no responsibility for any loss or damage that might result from reliance on the reported data or from its use.
LEARN MORE
Global Key Players in Preventive Medicine and Public Health
- Gilead
- GlaxoSmithKline
- EuroSciCon
- Merck & Co
- Novartis
- Roche
- Pfizer
- Johnson & Johnson
- Biogen Idec
- Amgen
- EuroScicon
- AstraZeneca
- Gilead Sciences
- Novo Nordisk
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Baxter
- Renovo
- Aventis Pharma
- Janssen-Cilag
- Daiichi Sankyo
- Actavis
- Spansules Pharmatech
- Aventis Pharma
- Alvogen
- Ipsen Developments
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Antisoma
- Vectura
- Genus
- BTG
- Eli Lilly & Co.
- Allergan
- Biogen
Top Preventive Medicine and Public Health Manufacturers
- Auxilium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Avadel Pharmaceuticals
- Avanir Pharmaceuticals
- EuroSciCon
- Avidas Pharmaceuticals
- Avion Pharmaceuticals, LLC
- Johnson & Johnson Medical
- JHC Healthcare Ltd
- Aytu BioScience, Inc.
- Actelion Pharmaceuticals
- Acura Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Adapt Pharma
- Adienne Pharma & Biotech
- Aegerion Pharmaceuticals
- Afaxys Pharmaceuticals
- Akorn, Inc.
- Bray Health & Leisure
- BSN Medical
- Cambridge Healthcare Supplies Ltd
- Ceuta Healthcare Ltd
- Torbet Laboratories Ltd
- Crookes Healthcare Ltd
- AbbVie and Biogen
- AbbVie and Genentech
- ABER Pharmaceuticals, LLC
- Acadia Pharmaceuticals
Distributors of Preventive Medicine and Public Health Products in UK and Europe
- Advance Holdings (UK) Ltd
- AERES Biomedical Ltd
- Aesculap Ltd
- ID Medical Group Ltd
- EuroScicon
- AFFINITI Research Products Ltd
- Agrimin Ltd
- Circle Health Ltd
- Akita Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- Ajinomoto Pharma Europe Ltd
- Alaris Medical Systems
- Alchemy Laboratories Ltd
- Alcon Laboratories Ltd
- Alfa Laval Ltd
- Menarini Diagnostics Ltd
- A1 Pharmaceuticals
- AAH Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- Micro Medical Ltd
- Care Management Group
- EKF Diagnostics
- Hayward Medical Communications
- Nuffield Health
Distributors of Preventive Medicine and Public Health Products in USA
- Amerisource Bergen
- Cardinal Health, Inc
- McKesson Corporation
- X-GEN Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Owens & Minor
- Henry Schein
- EuroSciCon
- Sinopharm Group
- H. D. Smith & Co.
- Pharmaceuticals (USA) Inc.
- ViiV Healthcare
- Genentech, Inc.
- Unichem Laboratories
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc., USA
- Collegium Pharmaceutical, Inc.
- Braintree Laboratories Inc.
- Octapharma USA, Inc.
- AstraZeneca
- Astellas Pharma US, Inc.
- Mead Johnson & Company, LLC
- Panacea Biotec Ltd
- Rubicon Research
- Alexion Pharmaceuticals
Hospitals in USA
- Mayo Clinic
- Johns Hopkins Hospital
- Mount Sinai Hospital
- Cedars Sinai Medical Center
- EuroSciCon
- Providence Kodiak Island Medical Center
- Blue Ridge Regional Hospital
- Laguna Honda Hospital and Rehabilitation Center
- Glendale Adventist Medical Center - Wilson Terrace
- Stanford Hospital
- University of California Davis Medical Center
- Wrangell Medical Center
- Bothwell Regional Health Center
- Grossmont Hospital
- Huntington Memorial Hospital
- Alamance Regional Medical Center
- Elmendorf AFB Hospital
- Santa Clara Valley Medical Center
- Lanterman Developmental Center
- Lac+Usc Medical Center
Top Preventive Medicine and Public Health Societies/Associations
- European society of preventive medicine
- British Geriatrics Society
- EuroSciCon
- England Preventive Medicine Society
- Society for Veterinary Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine (SVEPM)
- Joint British Society
- American Association of Physician Specialists
- European medical association
- Royal College of Midwives
- Royal College of Nursing
- European Union geriatric medicine society
- European lifestyle medicine association
- American Board of Emergency Medicine
- Aerospace medical association
- German Network for Evidence Based Medicine
- Association for prevention and research
- European Society of Clinical Microbiology
- Brazilian Medical Association
- The American Society for Preventive Cardiology
- Medical Society Consortium on Climate and Health
- International Academy of preventive medicine
- International Board for Medical Research and Studies
- Europe Preventive Medicine Organisation
- Italian Society of Hygiene
- Preventive Medicine and Public Health
Top UK/ USA/ Canada/North America Universities with Preventive Medicine and Public Health Research
- King's College London
- The University of Edinburgh
- EuroSciCon
- The University of Nottingham
- University of Birmingham
- The University of Manchester
- University of Cambridge
- University of Dundee
- University of Salford, Manchester
- Columbia University
- University of Pharma
- University of Mississippi
- University of Kentucky College of Public Health
- Cardiff University
- University of Sheffield
- Berkley Emory University
- Tulane University
- University of South Wales
- University of Oklahoma
- University of Portoc
- Boston University
- University of California, Berkeley
- University of Michigan
- University of Minnesota
- Loma Linda University School of Medicine
- East Carolina University Brody School of Medicine
- Baylor College of Medicine
- Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine
- University of Washington
- University of South Florida
- University of Nebraska Medical Center
- Oregon Health and Science University
- University of Michigan
- Yale University
- University of Oxford
- Imperial College London
- University of Toronto
- Uppsala University
- University of Lisbon
- University of St Andrews
- American University of Beirut
- Lebanese American University
- Tbilisi State University
- University of Hong Kong
- Howard University College of Medicine
- Wayne State University School of Medicine
- University of Colorado
Journals
- European Journal of Preventive Medicine
- American Journal of Preventive Medicine
- Journal of Public Health
- American Journal of Public Health
- International Journal of Public Health
- Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health
- Journal of Public Health Policy
- Public Health Nutrition
- Journal of Community Health
- Journal of Occupational Health Psychology
- International Health
- Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health
- Global Public Health
- Human Resources for Health
- Health Education Journal
- Population Health Management
- Journal of Aging and Health
- Canadian Journal of Public Health
- Public Health Reports
- Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal
- International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
- Health & Place
- Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
- Critical Public Health
- Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine
- Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine
- British Journal of General Practice
- The New England Journal of Medicine
- Annals of Family Medicine
- American Family Physician
- Canadian Family Physician
- American Journal of Medical Quality
- Women's Health Issues
- Health Education Journal
- Journal of Healthcare Management
- Journal of Health Economics
- Population Health Management
- Sociology of Health and Illness
- BMJ Quality & Safety
- Journal of Pediatrics
- Journal of Pediatric Health Care
- Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law
- Medical Care Research and Review
- International Journal of Women's Health
- Methods of Information in Medicine
- Journal of Pain and Symptom Management